 For some time now, Microsoft has been bolstering its suite of intelligent assistant and conversational bot solutions. First, Microsoft acquired Maluuba, a deep learning research lab for natural language understanding and machine learning, then Berkeley-based conversational AI specialist Semantic Machines, and last year around this time the acquisition of XOXCO, makers of a bot development studio.
For some time now, Microsoft has been bolstering its suite of intelligent assistant and conversational bot solutions. First, Microsoft acquired Maluuba, a deep learning research lab for natural language understanding and machine learning, then Berkeley-based conversational AI specialist Semantic Machines, and last year around this time the acquisition of XOXCO, makers of a bot development studio.
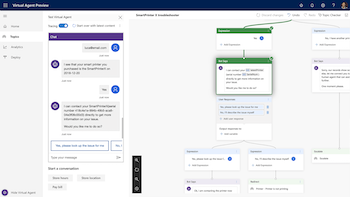
This impressive roster of conversational tools and technology has given the company momentum and credibility in its move to “democratize AI.” In that vein, earlier this week, Microsoft unveiled a public preview of Power Virtual Agents tool, a new way to make bot-building more accessible for customer support specialists and subject matter experts.
As a “no-code tool,” Power Virtual Agents allows users to build intelligent assistants via a graphical interface platform. The virtual agent technology is targeted at the citizen developer, leveraging natural language processing and machine learning to create natural groupings of intents and efficient tools to manage conversations. The system provides the most relevant information to its users based on limited sets of criteria and is intended for any use case including customer service, sales, marketing, and back-office employee productivity applications.
While the Power Virtual Agent platform is still in preview release, the city of Ottawa, Canada announced this week a new plan to pilot Microsoft’s technology to increase the accessibility of its 311 services. As a resource for Ottawa citizens, the intelligent assistant will answer questions about the city’s services and collect citizen feedback for ongoing improvement.
Indeed, using virtual agents and conversational AI to improve the citizen experience is a proven use case. This article from GCN cites an impressive case study from the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services division that launched a chatbot “Emma” which has “processed about 10.5 million requests from 3.3 million unique visitors that were typed in both English and Spanish … [including] an 89% success rate answering questions posed in Spanish and a 91% success rate for English.”
To further extend the capabilities of Power Virtual Agent, Microsoft announced the tools will integrate with Power Automate and Microsoft Flow. The platform can be used to create comprehensive dialog systems and automated intelligent assistants for Microsoft Teams, Facebook, Slack, etc. According to Microsoft, users can trigger actions based on bot data collection and provide advanced analytics to gain business insights and optimize business outcomes.
Categories: Conversational Intelligence, Intelligent Assistants, Articles, Mobile + Location

 Opus Research Welcomes Ian Jacobs as VP and Lead Analyst
Opus Research Welcomes Ian Jacobs as VP and Lead Analyst  United Airlines, TXU Energy, and Memorial Hermann Among Opus Research’s 2024 Conversational AI Award Winners
United Airlines, TXU Energy, and Memorial Hermann Among Opus Research’s 2024 Conversational AI Award Winners  Views from the NICE Analyst Summit: Introducing the Experience Continuum
Views from the NICE Analyst Summit: Introducing the Experience Continuum  Opus Research Announces 2023 Conversational AI Award Winners
Opus Research Announces 2023 Conversational AI Award Winners